
Gluten Intolerant, Sensitive or Celiac— Is it a trend or immune disorder?
Recently, being “Gluten Intolerant” has become a self-diagnosed trend, resulting in individuals cutting gluten from their diet completely. Whether this is from the idea that gluten (a protein found in wheat, rye and barley) is “unhealthy” or someone is experiencing symptoms similar to Celiac Disease found on a Google search, there is a better way to know exactly how your immune system reacts to gluten. We are here to straighten out this guessing game for you, and your doctors that seem to be baffled by your inconclusive tests or list of symptoms.
What if we told you that the answer was inside of you? Not just the painful stomachache you feel after a piece of toast, but in your genetics! Let us explain…
First it is important to note, the term gluten intolerance may refer to three types of human disorders: autoimmune Celiac disease (CD), allergy to wheat and non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS).
Who is most likely to have one of these gluten-related conditions?
Celiac Disease, wheat allergy and Non-celiac gluten sensitivity are all at higher risk to those with predisposed genetics to these conditions. If you have a first-degree relative (Parent, child, sibling) with one of these conditions, your risk is higher (1:10).
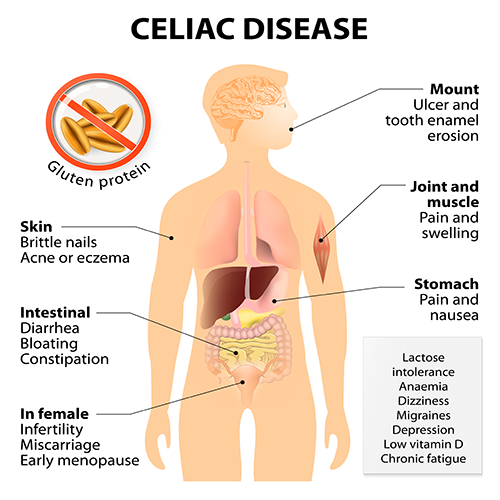
Common Celiac Disease symptoms to look out for
Most common symptoms found in children:
Most common symptoms found in adults:
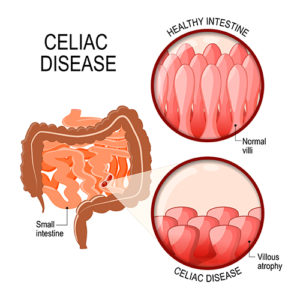
Also, there are cases of asymptomatic celiac disease patients, in which there are no complaints from the individual with CD but there is still evidence of damage to the small intestine [4].

How the DNA ConneXions® gluten sensitivity panel can help you take control of your health BEFORE symptoms occur.
The DNA ConneXions® Gluten Sensitivity test panel utilizes super floss to detect the presence or absence of the HLA tissue typing markers for DQ2 and DQ8 (specifically the markers HLA-DQB1*02, HLA-DQA1*0501, HLA-DQB1*0302 exon2 and HLA-DQB1*0302 exon3). The presence of any of these genetic markers is 95% predictive for gluten intolerance/sensitivity. The presence of all markers is 95% predictive for Celiac disease. Our gluten sensitivity test panel can help you discover health problems and take steps to improve your diet before symptoms occur.
If you, or someone you know, have a high risk of developing Celiac disease, allergy to wheat, or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, our test panel can provide insight into your genetics to aid you and your doctor in reaching diagnosis.
So is it a Trend? With predictions that 1:100 people and 1:10 of those who have first-degree relatives suffer from celiac disease, this trend is real. The good news is we have the resources to help people discover their likelihood of these conditions and allows those individuals to take the steps to adjust their diets accordingly.
Take control of your health today… Purchase your Gluten Panel HERE.
References:
DNACONNEXIONS.COM © ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 2024 | Issues with website? Contact Websnare, Inc.